Uploaded on 2017-01-05 by Dr. Madhura
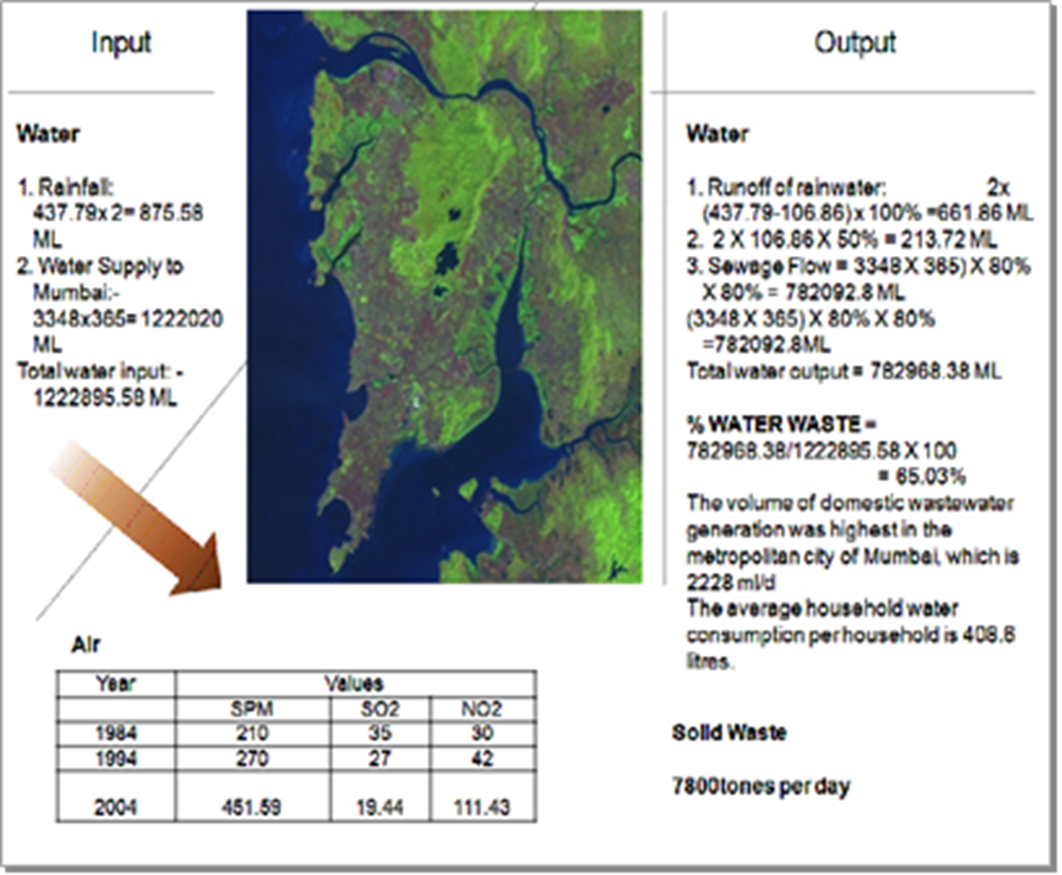
This information is a part of my research. Following Stocks and flows are identified for city of Mumbai. Water Population density Building Materilas Water Traditionally, a set of lakes provides drinking water to the city of Mumbai. Due to its geographical location, Mumbai is blessed with heavy monsoon and the lakes provide sufficient water to the city. The almost contiguous lakes of Tulsi, Vihar and Powai are the sources of water for Mumbai. According to the World Health Organisation, 100 litres of water per person per day is the minimum requirement. Water consumption per person is 90.4 litres 69 percent households in Mumbai are water deficient. Among slum dwellers, 72 per cent of households are water deficient. Population Density According to the 2011 census, The population of Mumbai has increased from 11.91 million in 2001 to 18.41 million in 2011. Greater Mumbai which had witnessed 30.47% growth in population during 1991-2001 has recorded 12.05% during 2001-2011.An additional 2-3 million ‘floating population’ also resides in Mumbai. The population density (about 27,209 people per sq. km.) is one of the highest in the world. Roughly 55% of the population resides in slums. Mumbai population has reached 18.4 million in 2011. Impact is • Disadvantages of high-density developments in terms of daylight access, wind tunneling and urban heat island effects Building Materials • High-rise structures often require materials (e.g. steel) with a higher embodied energy • The requirement of Bricks for Mumbai is about 40 lac bricks per day and therefore about 20 acre (4 hectares = 40,000m²) area top soil is used only for Mumbai for brick making.Impact is as below: • Removal of top fertile soil, adverse impact on agricultural produce. • High embodied energy materials have negative impact on surrounding ecosystems. • Disturbance in microclimatic conditions. • High energy materials will demand more operational energy Rapid and unplanned urban growth in Mumbai has resulted in • Land use changes • Subsequent changes in the hydrological fluxes in the urban watershed. Mumbai is India’s most populous city and the fourth largest agglomeration in the world.Looking in to the above mentioned stock and flows it is clear that Population is the biggest problem Mumbai is facing. Land is scarce. There is a tremendous pressure on the basic infrastructure and transport facilities of this city putting immense pressure on resources. The city is facing disasters like flood, climate change etc. The natural ecosystems of Mumbai are altered by manmade ecosystems. The population explosion is leading to increase in building sector and thereby resources like water and building materials.